Viruses
Viruses are very tiny – they are much smaller than bacteria or fungi . They measure only a few thousand millionths of a metre (nanometres).
All natural viruses cause disease including the common cold, influenza (flu), measles, mumps and rubella. They are not living cells themselves, and they can only reproduce inside other living cells.
Viruses can attack all different types of living organisms – they invade animal, plant and even bacterial cells. Different viruses attack specific cells – so the 'flu virus attacks the cells of the respiratory system while the virus which causes meningitis attacks the cells of the membranes which cover your brain.
Scientists have started to use viruses to benefit people. They are an important tool in genetic engineering. They are used to carry new genes into the DNA of the cells of other organisms.
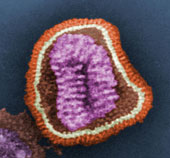
The flu virus
Photo provided by CDC/ Dr. Erskine. L. Palmer; Dr. M. L. Martin
The structure of viruses
- Protein coat
this attaches to and penetrates the host cell. It surrounds and protects the genetic material - Genetic material
This can be DNA or another similar chemical called RNA. It contains the information needed to take over the host cell DNA and make new viruses
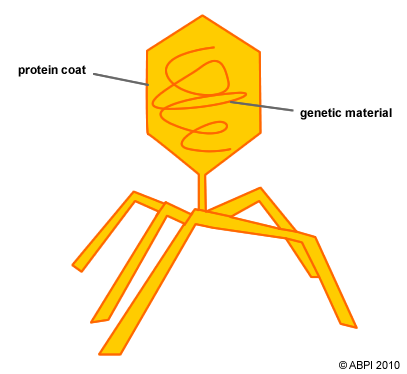
The structure of a virus